Creating an accessible bathroom that complies with the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA) is essential for ensuring that all individuals, regardless of their physical abilities, can navigate and use the space comfortably. ADA guidelines aim to provide equal access and usability in public and commercial restrooms, making it crucial for designers and builders to understand these requirements.
One of the primary considerations in ADA-compliant bathroom design is the layout. Sufficient space must be provided to accommodate individuals using mobility aids such as wheelchairs or walkers. This includes a clear path for movement and adequate turning space, typically requiring a minimum of 60 inches in diameter to allow for a full turn. The layout must also ensure that fixtures are positioned within easy reach, reducing the need for users to stretch or bend excessively.
The toilet area is a focal point in ADA bathroom requirements. Toilets should be installed at a height of 17 to 19 inches to facilitate ease of transfer from a wheelchair. Additionally, grab bars must be installed on the side and behind the toilet to provide support. These bars should be securely mounted and capable of supporting at least 250 pounds. Clear space in front of the toilet must also be maintained to allow for safe transfers.
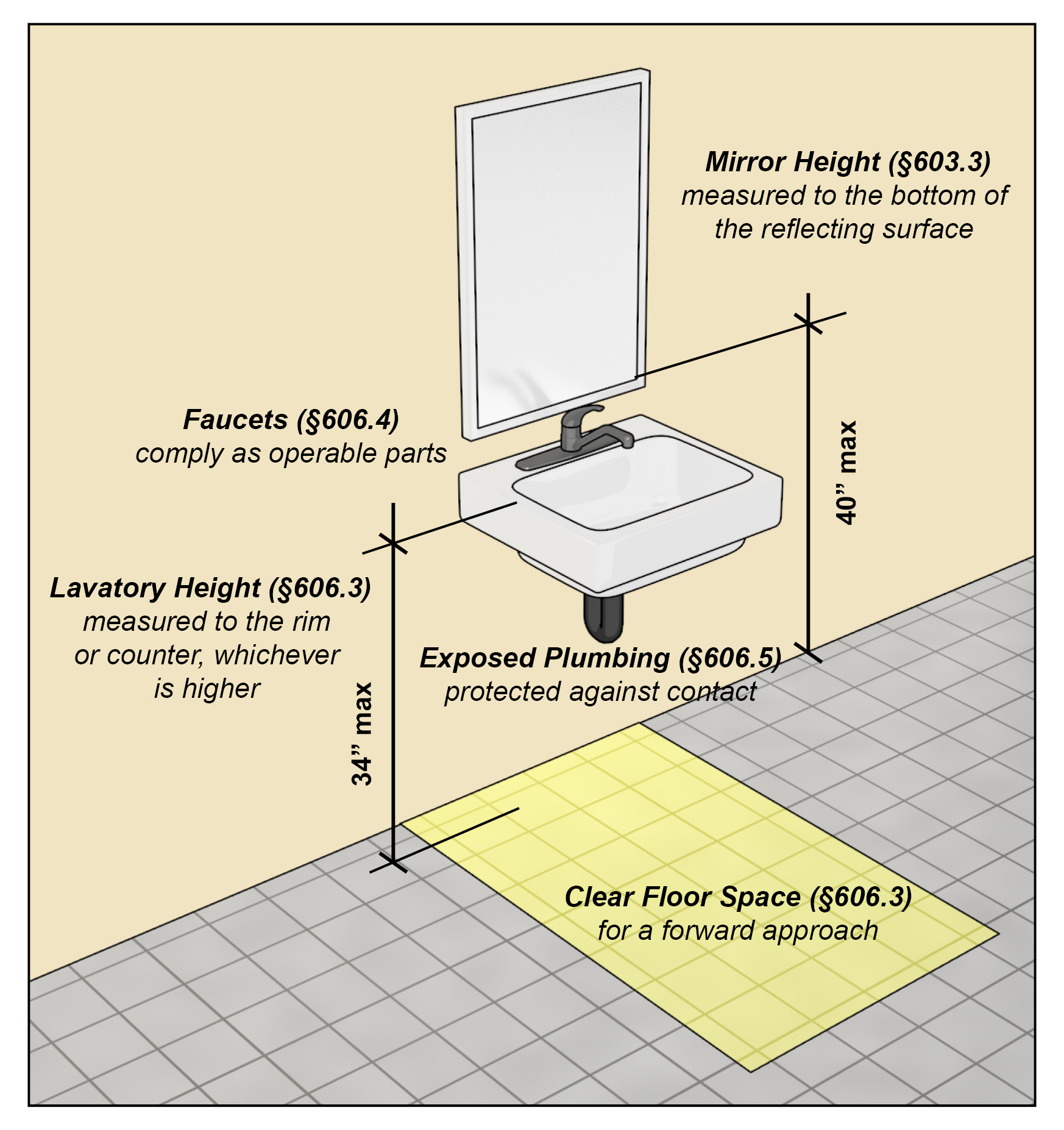
Sinks in an ADA-compliant bathroom should be accessible as well. The height of the sink should be no more than 34 inches from the floor, allowing for wheelchair access underneath. Faucets should be easy to operate, preferably using lever handles or motion sensors to eliminate the need for grasping. Additionally, there should be a clear floor space beneath the sink to accommodate wheelchairs, ensuring users can approach comfortably.
In terms of shower and bathing facilities, ADA guidelines specify the need for accessible showers with no thresholds. A roll-in shower design is preferred, allowing users to enter without needing to step over a barrier. Grab bars should also be installed in the shower area for safety, and a fold-down seat can provide additional convenience. For bathtubs, an accessible design includes built-in seating and grab bars to assist users in getting in and out safely.
Lighting is another critical aspect of ADA bathroom requirements. Adequate lighting should be provided to ensure visibility and safety. Light switches should be positioned within reach, typically between 15 to 48 inches from the floor, allowing users to operate them without difficulty. Additionally, using contrasting colors for walls and fixtures can enhance visibility for individuals with visual impairments.
Signage is important for informing users about accessible features within the bathroom. Signs indicating the location of accessible stalls, sinks, and other facilities should be clear, easy to read, and placed at appropriate heights. Braille and tactile elements should be included for individuals with visual impairments, ensuring that all users can navigate the space effectively.
Finally, maintaining cleanliness and accessibility is vital. Regular maintenance checks should ensure that all fixtures are in working order and that pathways are free from obstructions. This attention to detail not only complies with ADA requirements but also promotes a welcoming environment for all individuals.
In summary, understanding learn about ada vanity requirements here is essential for creating spaces that are accessible to everyone. By focusing on layout, fixture placement, safety features, and appropriate signage, designers can ensure that bathrooms are not only functional but also inclusive. Complying with these guidelines enhances the usability of facilities and fosters an environment where all individuals can feel comfortable and independent.
